Borehole Solutions
Our Borehole Solutions service is a complete end-to-end offering designed to provide you with reliable access to clean and sustainable water. Here is an outline of the process, detailing every step involved:
Borehole Solutions
Our Borehole Solutions service is a complete end-to-end offering designed to provide you with reliable access to clean and sustainable water. Here is an outline of the process, detailing every step involved:
Step 1: Hydrogeological Survery
The Hydrogeological Survey is the first and most critical step in the borehole drilling process. It involves a detailed scientific study to determine the most suitable location for drilling a borehole. This step ensures that the project is both technically sound and cost-effective, minimizing the risk of drilling in areas with insufficient or inaccessible groundwater.
Preliminary Assessment:
- We begin by gathering data about the proposed site, including its geographical, geological, and climatic conditions.
- This involves analyzing maps, satellite imagery, and historical data of the area to identify water-bearing zones.
Field Investigation:
- Our hydrogeologists visit the site to conduct a thorough examination of the terrain and soil.
- They use specialized tools and techniques, such as resistivity surveys, to detect underground water-bearing formations (aquifers).
- This step includes measuring soil permeability and evaluating the depth and thickness of the aquifer to determine the ideal drilling point.
- Aquifer Analysis:
- The team studies the aquifer's recharge rate, water quality, and storage capacity to ensure it can sustainably meet the client’s needs.
- This analysis helps in determining the depth of the borehole and the type of pump required.
- Report Generation:
- A detailed report is prepared, including findings from the survey, recommended drilling locations, and depth specifications.
- The report also outlines potential risks and mitigation strategies to ensure the project’s success.
Importance of a Hydrogeological Survey:v
- Accuracy: Ensures the borehole is drilled in the most water-rich area. Cost-Effectiveness: Prevents unnecessary expenses on failed drilling attempts.
- Sustainability: Confirms the aquifer's ability to meet water demand without overexploitation.
- Safety: Identifies potential geological risks, such as unstable soil or contamination sources.
By conducting a comprehensive Hydrogeological Survey, we lay the foundation for a successful and efficient borehole, ensuring long-term water access and client satisfaction.
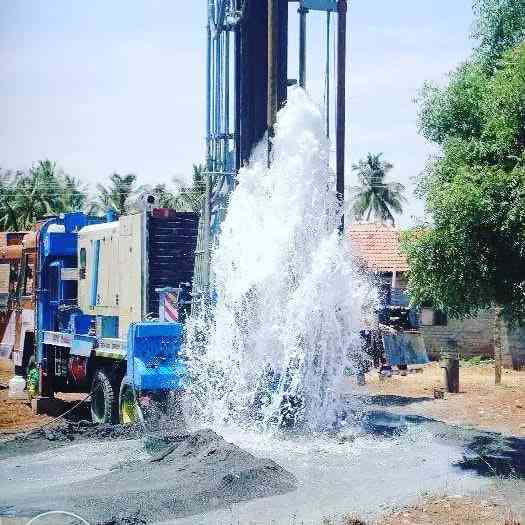

Step 2: Borehole Drilling
Borehole drilling is a critical stage in the process of accessing underground water. At Greenlands Drill Kenya, we utilize advanced, state-of-the-art drilling equipment to ensure precision and efficiency. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
- Site Preparation:
- Once the ideal drilling location is identified during the hydrogeological survey, the site is prepared for drilling. This includes clearing any obstacles and setting up the drilling rig and necessary equipment.
- Drilling Process:
- Our team begins by drilling a pilot hole to confirm the exact depth and structure of the aquifer.
- Depending on the geological conditions, we use rotary, percussion, or air drilling methods to reach the water-bearing layer (aquifer).
- Throughout the drilling process, we monitor the borehole depth, rock formation, and drilling fluid circulation to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Cuttings Analysis:
- As drilling progresses, rock and soil cuttings are analyzed to confirm the presence of water-bearing zones and aquifer depth. This step ensures that we target the most productive section of the aquifer.
- Depth Customization:
- The borehole is drilled to the recommended depth based on water demand and aquifer capacity. This customization ensures a reliable and long-lasting water source.
- Environmental Protection:
- To minimize environmental impact, we adhere to strict environmental guidelines. Drilling fluids and debris are carefully managed and disposed of properly.
- Preliminary Water Yield Testing:
- Once the target aquifer is reached, a preliminary test is conducted to assess the borehole's yield and confirm the presence of water.
At Greenlands Drill Kenya, we emphasize quality, precision, and environmental responsibility throughout the drilling process. This ensures that the borehole is not only efficient but also sustainable and capable of meeting your long-term water needs.
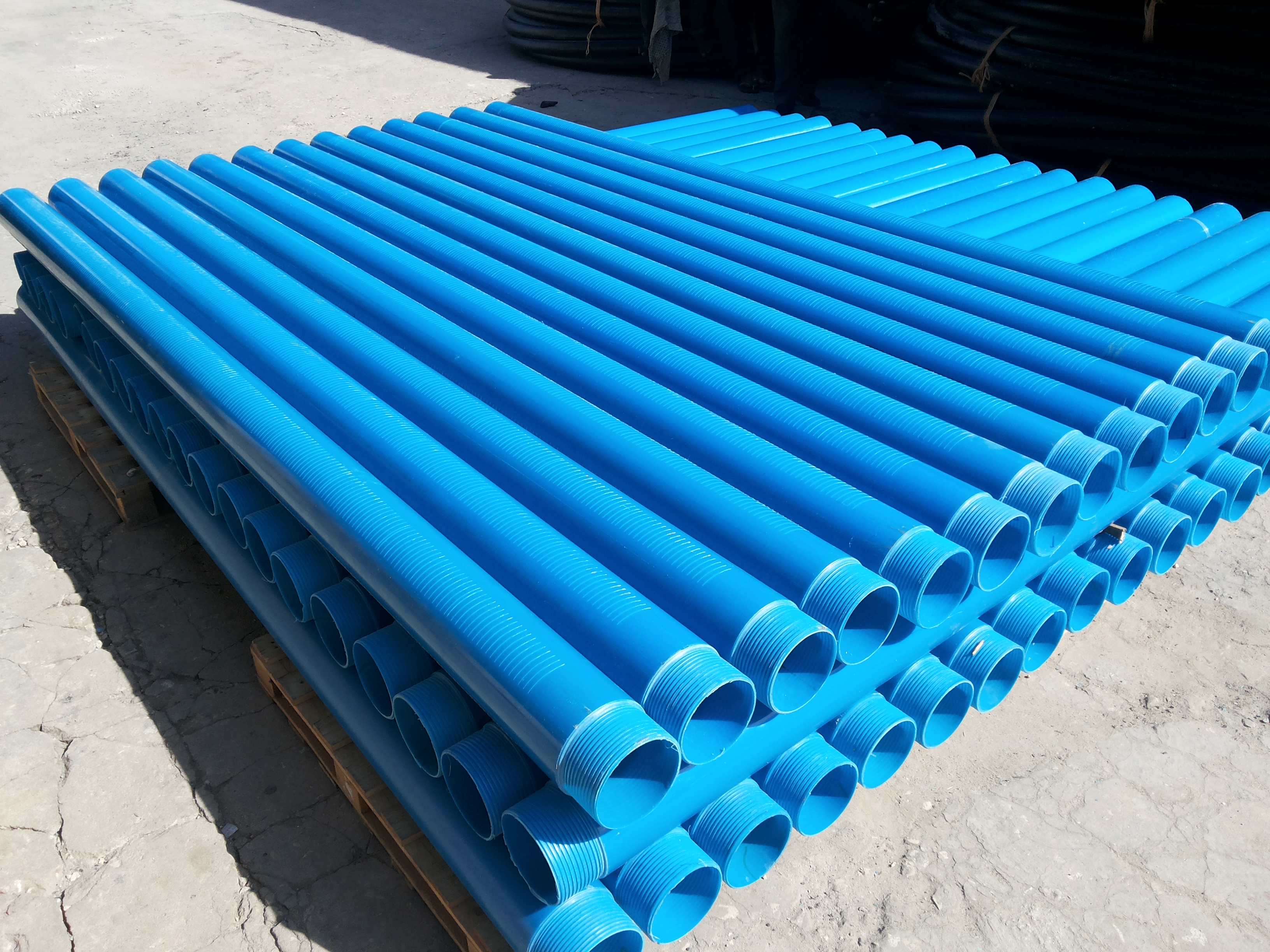

Step 3: Casing and Well Construction
- After the drilling process is complete, the borehole needs to be properly secured to ensure its structural integrity and prevent contamination. This is achieved through the casing and well construction process, which involves the following steps:
a. Installation of Casing Pipes:
High-quality casing pipes, typically made of PVC or steel, are inserted into the drilled borehole. These pipes serve as a protective lining, preventing the walls of the borehole from collapsing over time due to soil and geological pressures.
- The casing also provides a smooth pathway for water to flow and prevents loose soil or debris from entering the borehole.
b. Screen Installation:
- In aquifer zones (water-bearing layers), we install specially designed screen sections of the casing. These screens allow water to flow into the borehole while filtering out sand, silt, and other sediments, ensuring the extracted water is clean and sediment-free.
- The type and size of the screen are selected based on the geological conditions identified during the hydrogeological survey.
c. Grouting:
- Grouting is a critical step in sealing the space between the casing and the surrounding borehole wall. This is done using cement or bentonite-based materials, creating a secure seal that prevents surface water, contaminants, or pollutants from seeping into the borehole.
- This seal also strengthens the borehole structure, making it more durable over time.
d. Gravel Packing (if necessary):
- In some cases, a gravel pack is added around the screen section. This involves placing clean, uniform-sized gravel around the screen to further filter out fine particles and enhance the borehole's yield. It also stabilizes the borehole in loose or unconsolidated formations.
e. Headworks Installation:
- The casing is extended slightly above ground level, where a wellhead is installed. The wellhead protects the borehole opening and prevents debris, animals, or unauthorized access from contaminating the water supply.
By combining these measures, the casing and well construction process ensures that the borehole is stable, secure, and capable of delivering clean, reliable water for years. It also safeguards the long-term efficiency and quality of your water system.
Step 4: Test Pumping and Yield Analysis
- Test pumping is a critical step in the borehole development process to assess its capacity and ensure its long-term efficiency. This process involves temporarily installing a pump in the borehole to extract water while monitoring key parameters such as flow rate, drawdown, and recovery time. Here's a detailed breakdown of the process:
- Flow Rate Testing:
- The borehole is pumped at varying flow rates to determine the maximum sustainable yield without overextraction or causing undue stress on the aquifer.
- This ensures that the borehole can provide a consistent supply of water over time without depleting the source.
- Drawdown Measurement:
- Drawdown refers to the drop in water level within the borehole during pumping. By measuring the drawdown, we assess how efficiently the borehole delivers water.
- Excessive drawdown might indicate inadequate aquifer recharge or an improperly sized borehole.
- Recovery Rate Analysis:
- After pumping is stopped, the water level recovery time is measured. A fast recovery rate indicates a robust aquifer, while slow recovery may suggest limited recharge capacity.
- Aquifer Characteristics Evaluation:
- Test pumping provides valuable data about the aquifer, including permeability, transmissivity, and storage coefficient. These factors help determine the long-term sustainability of the borehole.
- Pump Sizing Recommendations:
- Based on the results of test pumping, we recommend the appropriate pump size and type (solar, generator, or electric-powered) that matches the borehole's capacity and your water demand.
By conducting thorough test pumping and yield analysis, we ensure that the borehole system is designed for optimal performance, preventing overpumping, minimizing energy costs, and prolonging the lifespan of the entire water supply system.
- Flow Rate Testing:
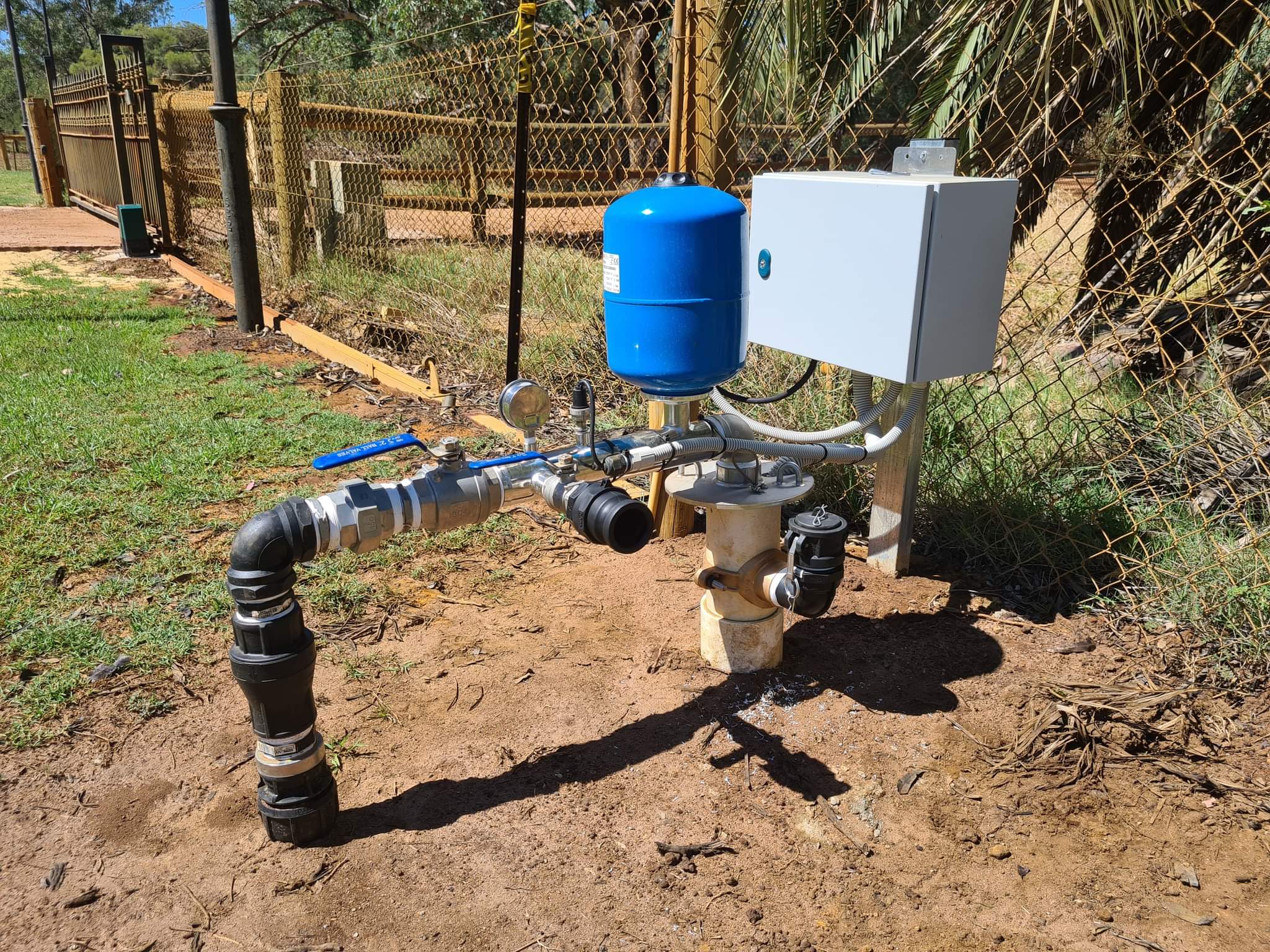

Step 5: Pump Installation
- Once the borehole is successfully drilled and tested for yield, the next critical step is pump installation, which determines the efficiency and reliability of water extraction. We offer three types of pump solutions, each designed to meet specific needs based on power availability, water demand, and environmental conditions. Here’s a breakdown of each option:
Solar-Powered Pumps:
Solar-powered pumps are an ideal choice for areas with ample sunlight and no reliable electricity supply. These pumps are powered by photovoltaic solar panels, converting sunlight into electricity to run the pump.
- Benefits:
- Eco-friendly: They utilize renewable energy, reducing your carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Cost-effective in the long term: After the initial installation, there are minimal operational costs, as sunlight is free.
- Low maintenance: Solar pumps require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan, especially in off-grid locations.
- Remote operation: Perfect for locations without access to grid power or where grid connection is expensive or impractical.
- Considerations:
- Solar pumps require sufficient solar energy, meaning they are most effective in regions with adequate sunlight.
- They are ideal for low to moderate water demands, as they may not be as powerful as generator-powered pumps for high-yield boreholes.
Generator-Powered Pumps:
For areas where electricity is unstable, unavailable, or expensive, generator-powered pumps offer a reliable alternative. These pumps are powered by either a diesel or petrol generator, making them versatile for a range of locations.
- Benefits:
- Dependable in any location: They can be used in remote areas or places where grid electricity isn’t accessible.
- High power output: Generator pumps are capable of pumping larger volumes of water, making them suitable for higher-yield boreholes or larger water demands.
- Immediate power source: Unlike solar-powered systems, generators don’t rely on sunlight, providing consistent pumping during all hours of the day and in any weather condition.
- Considerations:
- Fuel costs: Fuel consumption is an ongoing cost, and prices may fluctuate.
- Maintenance requirements: Generators require regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and fuel management.
- Noise and emissions: Generators can be noisy and emit pollutants, which may not be suitable for all environments.
Electric-Powered Pumps:
If the borehole is located in an area with a reliable and stable electricity supply, electric-powered pumps are an excellent option. These pumps are connected directly to the local grid, and their operation is smooth and consistent.
- Benefits:
- Efficient and powerful: Electric pumps are highly efficient and capable of handling large volumes of water, making them ideal for high-yield boreholes or areas with high water demand.
- Minimal operational costs: Electricity is typically cheaper than fuel, and the long-term cost of operation is relatively low compared to generator-powered systems.
- Quiet operation: Electric pumps are quieter than generators, making them ideal for residential areas.
- Low maintenance: Electric pumps generally require less maintenance than generator-powered systems.
- Considerations:
- Power dependency: They rely on a consistent and reliable electricity supply, so in areas with frequent outages, additional backup power may be needed.
- Installation costs: For remote areas, the cost of bringing electricity to the site can be high, and it may take time to establish a connection to the grid.
Installation Process:
- Pump Sizing and Selection: Based on the borehole yield, water demand, and power source, we determine the correct size and type of pump for your specific needs. This ensures the system operates efficiently without overloading the pump.
- Piping and Electrical Connections: Once the pump type is selected, we connect it to the borehole, ensure proper piping, and make the necessary electrical or generator connections for operation.
- Testing: After installation, we conduct comprehensive tests to ensure the pump is extracting water effectively and operating within the designed parameters.
By selecting the appropriate pump system based on your specific location and requirements, we ensure the long-term functionality, sustainability, and efficiency of your borehole water supply.
- Benefits:
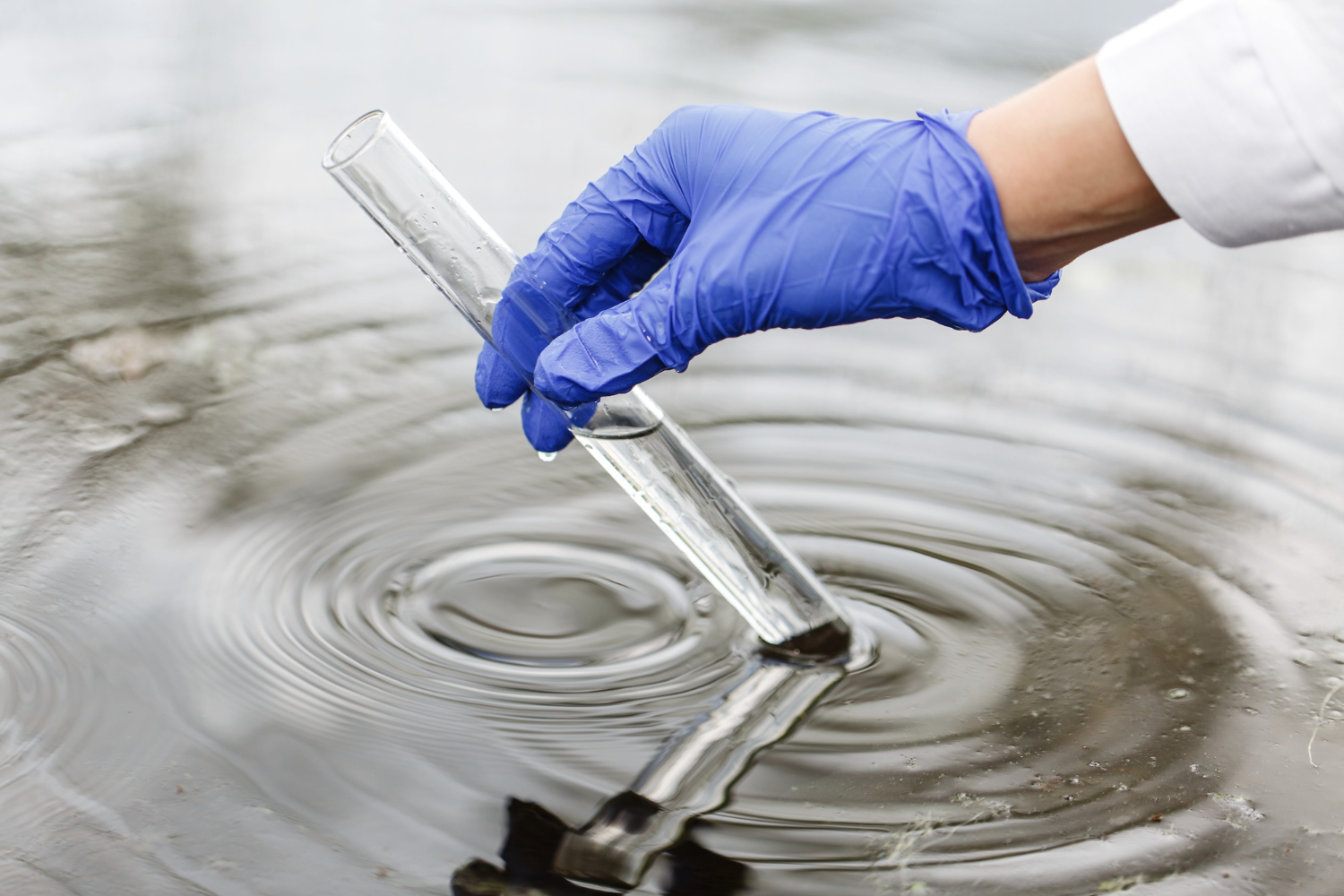

Step 6: Water Quality Testing
Water quality testing is a critical part of the borehole installation process. It ensures that the water extracted from the borehole is safe for consumption and use. Here's a detailed breakdown of this step:
- Initial Sample Collection:
After drilling and pump installation, our technicians collect water samples directly from the borehole at different stages (before and after pump testing) to assess the quality of the water. The sample collection is done in a controlled manner to avoid contamination, ensuring accurate results. - Laboratory Analysis:
The collected water samples are sent to an accredited laboratory for comprehensive analysis. Various parameters are tested, including:- pH Levels: Determines the acidity or alkalinity of the water, which impacts its suitability for drinking and irrigation.
- Total Dissolved Solids (TDS): Measures the concentration of dissolved substances, including salts and minerals, to ensure the water is within acceptable limits for human consumption.
- Microbiological Testing: Checks for harmful pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites, to ensure the water is safe for drinking and domestic use.
- Heavy Metals: Tests for contaminants like lead, arsenic, or mercury, which could pose health risks.
- Nitrate and Nitrite Levels: Elevated levels can indicate pollution from agricultural runoff or septic systems, which can be harmful to health.
- Turbidity: Measures the cloudiness of the water, which indicates the presence of suspended particles that may affect the water's quality.
- Results Evaluation:
Once the laboratory tests are completed, we review the results to determine whether the water meets the required standards for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. If the water quality is not up to standard, we recommend solutions such as filtration, chemical treatments, or additional purification steps. - Reporting and Recommendations:
We provide a detailed report of the water quality test results, including any contaminants found and their potential impact. If necessary, we offer recommendations for improving the water quality, such as installing water treatment systems (e.g., UV sterilizers, reverse osmosis filters, or chemical dosing systems). - Post-Installation Monitoring:
After the borehole is in operation, periodic water quality testing is recommended to ensure the water remains safe over time. Changes in the water table or environmental factors can sometimes affect water quality, so ongoing monitoring ensures the system continues to meet health and safety standards.
Water quality testing is essential not only to confirm that the water is safe for use but also to guarantee that your borehole is a long-term, reliable source of clean water. This step ensures that your investment provides value and safety to you and your community.

Step 7: Maintenance and Repairs:
To keep your borehole functioning efficiently, we provide ongoing maintenance and repair services. From routine inspections to fixing issues, our team ensures your borehole remains operational for years to come.
